Fabulous Info About Can You Run 240V Without Neutral
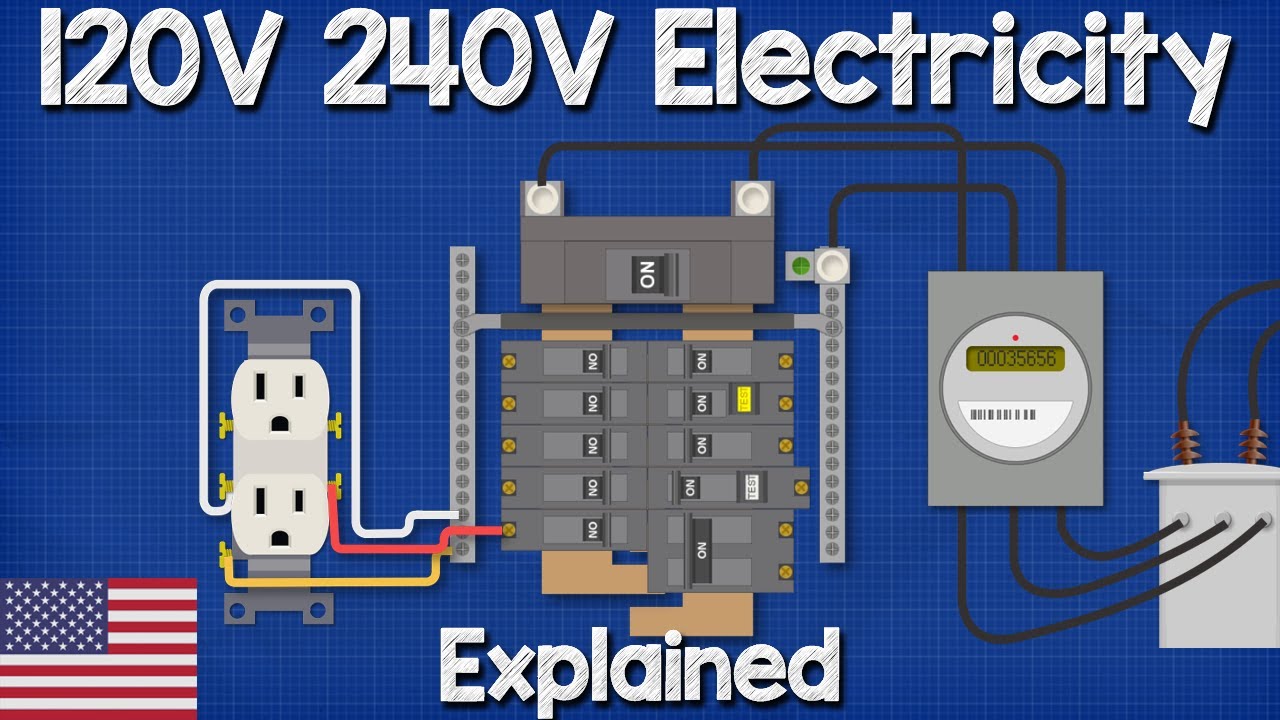
How To Connect A 240 Volt Outlet
Unlocking the Secrets of 240V Circuits
1. Understanding the Basics of Electrical Circuits
So, you're diving into the world of electrical circuits, specifically the 240V variety, and you've stumbled upon a burning question: "Can you run 240V without a neutral?" It's a valid question, and the answer, like most things electrical, isn't a simple yes or no. It depends entirely on the specific application and the type of load you're dealing with. Think of it like baking a cake; you can't just randomly omit ingredients and expect a delicious result, right? Same goes for electricity.
In essence, understanding the neutral wire requires understanding the role it plays in a balanced electrical system. Imagine electricity as water flowing through pipes. The hot wires are like the supply lines bringing the water to your faucet, and the neutral wire is the return pipe allowing the water to flow back to the source. Without that return path, the water (electricity) can't complete its circuit, and things just won't work.
Many 240V appliances, especially those using resistive heating elements like electric ovens, dryers, or water heaters, operate perfectly fine without needing a neutral. These devices use the two hot wires, each carrying 120V relative to ground, to create the 240V potential difference that powers them. It's like having two strong water pumps working together to power a single, larger water wheel.
However, some 240V appliances do require a neutral wire. This is typically the case when the appliance also includes 120V components. Think of a 240V dryer with a 120V motor for the drum or a 120V electronic control panel. The neutral provides the return path for these 120V circuits. Bypassing the neutral in such cases could lead to some seriously unhappy (and potentially fried) components. It's like trying to run a complex machine with only half the necessary power sources — definitely not a recipe for success.

240V Sub Panel Wiring Diagram EdenBengals
The Devil's in the Details
2. Analyzing Load Types and Circuit Configurations
Now, let's delve into some scenarios where that neutral wire becomes absolutely crucial. Imagine you're wiring up a modern electric range. While the heating elements themselves might run solely on 240V, that fancy digital display, the timer, and perhaps even an internal light likely operate on 120V. To power these components, the appliance needs a neutral wire to complete the 120V circuit.
Another common situation is with certain types of 240V outlets. Sometimes, you'll find 240V outlets that also provide a 120V receptacle on the same circuit. This is often seen in workshops or garages where you might have a heavy-duty tool running on 240V and need a standard 120V outlet for a lamp or battery charger. In this case, the neutral is essential for providing that 120V supply. Think of it as a multi-tool; it needs all its components to function fully.
Ignoring the need for a neutral in these circumstances can lead to a variety of problems. At best, the 120V components simply won't work. At worst, you could overload the circuit, damage the appliance, or even create a fire hazard. Electricity is like a wild animal — treat it with respect and follow the rules.
Consider the alternative. Imagine a scenario where an appliance designed to use a neutral is forced to operate without one. This can create unbalanced loads, where the voltage on each of the 120V legs is unevenly distributed. This uneven distribution can then cause one leg to overheat and lead to component failure or even a fire. A properly installed neutral protects your electrical components from unbalanced loads, ensuring a smoother and safer operation of the electrical circuits.

Safety First
3. The Importance of Proper Wiring Practices
While we're discussing neutrals, it's vital to touch on the related concepts of grounding and bonding. These aren't the same as a neutral wire, but they play a critical role in electrical safety. Grounding provides a path for fault current to flow back to the source, tripping a breaker and preventing electrical shock. Bonding ensures that all metallic parts of an electrical system are at the same potential, reducing the risk of electrocution.
Never, ever confuse a neutral wire with a ground wire or attempt to use one in place of the other. They have distinct functions and are wired differently for a reason. A neutral wire carries current under normal operating conditions, while a ground wire only carries current during a fault. Swapping them can create a hazardous situation.
Proper wiring practices are paramount when dealing with 240V circuits. Always consult the appliance's wiring diagram and local electrical codes before making any connections. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, hire a qualified electrician. It's not worth risking your safety or property to save a few bucks.
Think of it like this: electrical safety is like wearing a seatbelt. You might not think you need it on every trip, but it's there to protect you in case something goes wrong. Proper grounding and bonding are your electrical seatbelts, ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system. Without them, it's just a matter of time before something bad happens.

How To Wire A Subpanel? Main Lug Installation For 120V/240V
When in Doubt, Check it Out
4. Consulting the Experts (and the Manual)
So, how do you determine if a particular 240V appliance needs a neutral wire? The best approach is to consult the appliance's wiring diagram. This diagram, usually found on the appliance itself or in the owner's manual, will clearly show whether a neutral connection is required. It's like having a roadmap for your electrical journey, guiding you safely to your destination.
Look for symbols indicating 120V components within the appliance. If you see these, it's a strong indication that a neutral wire is needed. Also, pay attention to the type of plug or receptacle used. A 240V receptacle with four prongs (two hots, a neutral, and a ground) almost always requires a neutral connection. A three-prong receptacle (two hots and a ground) typically doesn't.
If you're still unsure, don't hesitate to contact the appliance manufacturer or a qualified electrician. They can provide expert guidance based on the specific appliance model and your local electrical codes. It's always better to be safe than sorry when dealing with electricity.
Remember, even if you've wired up similar appliances before, it's crucial to check the wiring diagram each time. Appliance designs can change, and assuming you know how something is wired can lead to dangerous mistakes. Keep your circuits and your family safe by double checking every connection. The best way to think about it is like this: its better to double check than to double the risk.
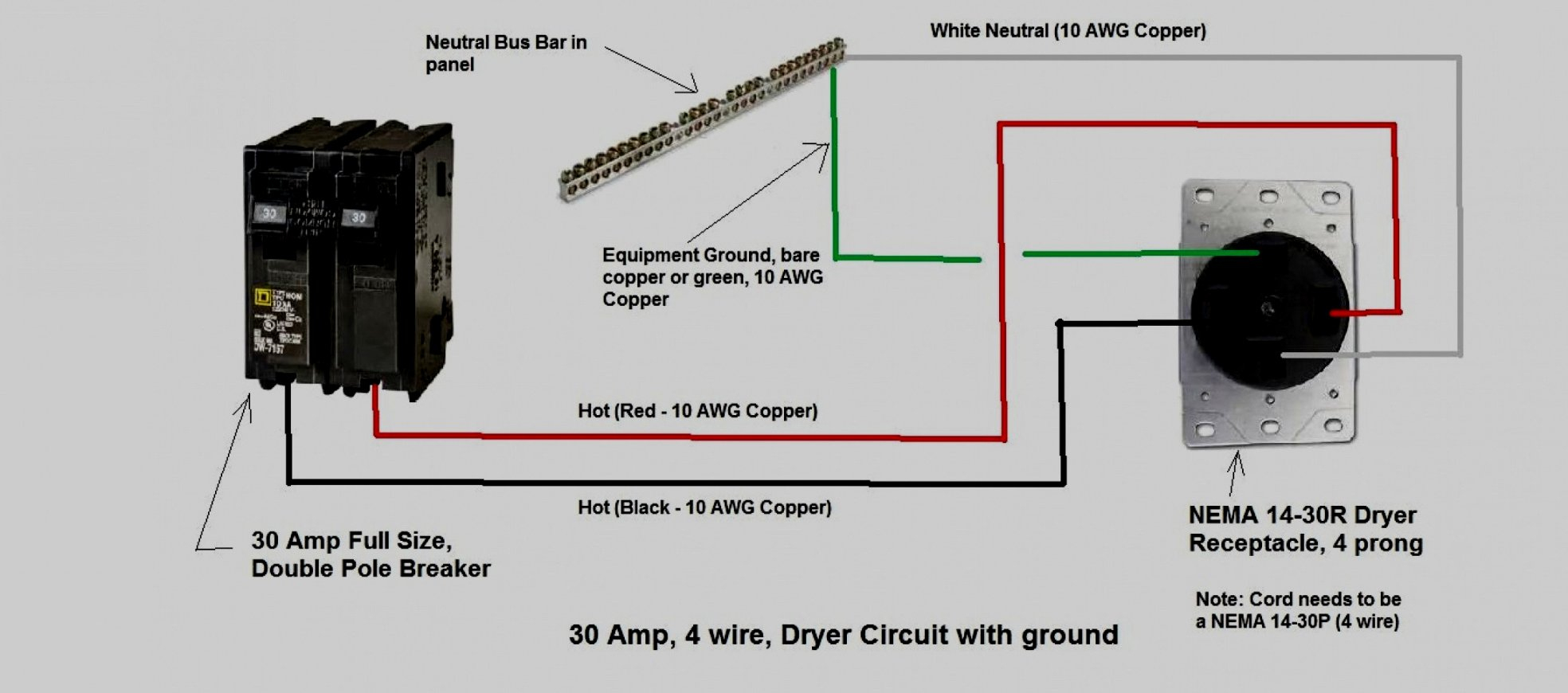
Wiring Diagram For 240 Volt Outlet
Real-World Examples
5. Putting Theory into Practice
Let's look at some real-world examples to solidify your understanding. A typical electric clothes dryer often requires a neutral wire. The heating element runs on 240V, but the motor that turns the drum and the timer usually operate on 120V. Therefore, a four-wire connection (two hots, a neutral, and a ground) is needed. Older dryers might have only three wires, relying on a bonded neutral and ground, but this is no longer considered safe and should be updated.
On the other hand, a dedicated 240V electric water heater typically doesn't require a neutral. It consists solely of resistive heating elements that operate on 240V, so a three-wire connection (two hots and a ground) is sufficient. Similarly, a 240V window air conditioner usually doesn't need a neutral, as it only contains components that operate on 240V.
However, appliances are constantly evolving. Some newer appliances, even those traditionally wired without a neutral, may now incorporate electronic controls or other 120V components, requiring a neutral connection. This highlights the importance of always checking the wiring diagram before making any connections.
Think of it like this: Electrical systems are like snowflakes; no two are exactly the same. While there are some common patterns and general rules, each installation has its own nuances and peculiarities. The key is to approach each project with diligence, a willingness to learn, and a healthy respect for the power you're dealing with. So, next time you're tackling a 240V circuit, remember the neutral question. The answer is out there, waiting to be discovered!
