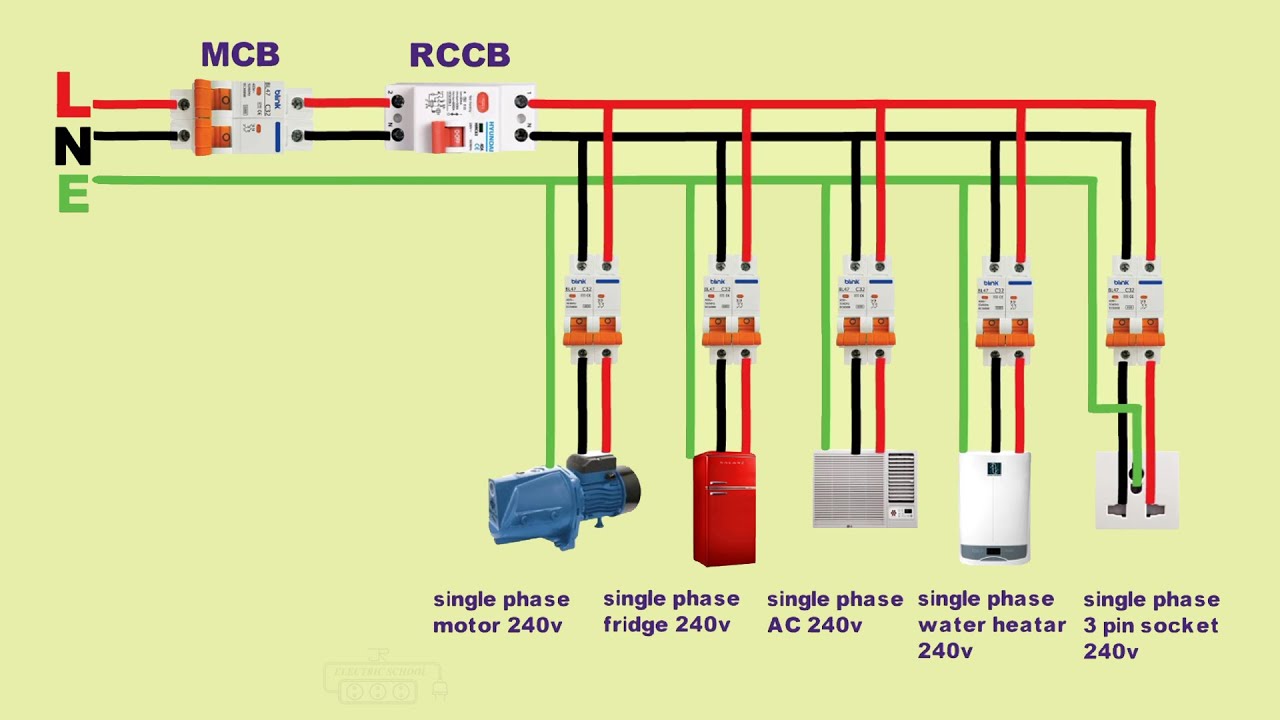
Outstanding Tips About How To Convert 3 Phase Single-phase 240v

Single Phase 480v To 240v Transformer
Understanding the Need
1. Why Bother with Phase Conversion?
Alright, let's cut to the chase. You've got a snazzy piece of equipment that needs 240V single-phase power, but all you've got humming around is a 3-phase system. Maybe you're expanding your workshop, adding a heavy-duty appliance to your home, or trying to power specialized tools. The problem is, these power systems speak different languages, and we need a translator. This conversion isn't just about plugging things in; its about ensuring your equipment runs safely and efficiently without frying anything or causing a power surge that could leave you in the dark — literally!
Think of it like this: you've got a recipe that calls for specific ingredients in specific proportions. Trying to wing it with whatever's in the fridge could lead to a culinary disaster. Similarly, feeding your equipment the wrong type of power can be a costly mistake. Converting from 3-phase to single-phase 240V helps match the power supply to the appliance's requirements, optimizing performance and extending its lifespan. No one wants to replace expensive machinery because of a simple power mismatch, right?
Beyond functionality, safety is paramount. Three-phase systems, while incredibly powerful, can be a bit too much for smaller single-phase appliances to handle directly. Overloading a single-phase circuit with 3-phase power can cause serious electrical hazards, including overheating, short circuits, and even fires. Properly converting to the correct voltage and phase is essential for preventing accidents and maintaining a safe operating environment. It's always better to be safe than sorry, especially when dealing with electricity.
Lastly, efficiency plays a crucial role. Mismatched power supplies can lead to energy waste. Imagine trying to fill a small glass with a firehose — most of the water would just splash everywhere. Similarly, an inefficient power setup results in lost energy, driving up your electricity bill and potentially damaging your equipment over time. Conversion ensures that the right amount of power is delivered where it's needed, minimizing waste and saving you money in the long run. It's a win-win situation: better performance, safer operation, and lower energy costs.

Diving into the Options
2. Methods for Converting 3-Phase to Single-Phase
Okay, so we know why we need to convert. Now for the how. There are a few common approaches to tackle this, each with its own pros and cons. The best method depends on your specific needs, budget, and the amount of power you require. Were going to look at a few of the most popular and effective ways to make this conversion happen without electrocuting ourselves.
First up, let's talk about using a rotary phase converter. Think of this as a mini-generator that takes 3-phase power and spins it into single-phase. These converters are great for handling larger loads, like powering a big workshop or running several machines simultaneously. They're generally more expensive upfront, but they can be more cost-effective in the long run if you need a significant amount of single-phase power. Plus, they tend to provide cleaner power than some other methods, which is always a good thing for sensitive equipment.
Next, we have static phase converters. These are simpler and less expensive than rotary converters. They use capacitors to create a pseudo-single-phase output from the 3-phase input. However, static converters are usually only good for starting motors and arent suitable for continuous operation under heavy loads. They also tend to produce a less balanced voltage, which can affect the performance of some equipment. So, if you just need to get a motor spinning, a static converter might be the way to go, but for more demanding applications, you might want to consider other options.
Finally, there's the simplest (but often least practical) option: using a transformer. If your 3-phase system includes a delta-wye transformer, you might be able to tap into one leg of the wye configuration to get 240V single-phase. This method is heavily dependent on your existing electrical setup, and its crucial to ensure that you dont overload any of the transformer's phases. This method usually requires a professional electrician to ensure it is done correctly and safely. It is not a solution for many situations and should be carefully evaluated.

Safety First
3. Don't Become a Human Fuse!
Before you even think about touching wires, let's talk safety. Electricity is like a grumpy cat — treat it with respect, or it will bite! Working with 3-phase power is not a DIY project for the faint of heart. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, or if you don't have the proper training and experience, hire a qualified electrician. Seriously, your life is worth more than saving a few bucks.
Always, always, always disconnect the power before working on any electrical equipment. And I mean really disconnect it. Flip the breaker, pull the fuse, whatever it takes to make absolutely sure that theres no current flowing. Then, use a voltage tester to confirm that the circuit is dead. Double-check, and then check again. Trust me, you don't want to learn the hard way that the power was still on.
When you're working with electrical equipment, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes safety glasses, insulated gloves, and non-conductive footwear. These items can help protect you from electric shock, arc flash, and other hazards. Make sure your PPE is in good condition and properly rated for the voltage you're working with. Don't skimp on safety gear; it's the only thing standing between you and a potentially deadly accident.
Finally, make sure you understand the electrical codes and regulations in your area. These codes are designed to ensure the safety of electrical installations and prevent accidents. Failure to comply with these codes can result in fines, penalties, and, more importantly, unsafe conditions. If you're not sure about something, ask an electrician or building inspector for clarification. It's better to be informed than to risk violating the law or endangering yourself and others.

Selecting the Right Converter
4. Choosing the Right Conversion Method
So you've got options, right? Rotary, static, maybe even tapping a transformer. But which one is the right one for you? Its like picking the right wrench for the job; using the wrong tool can lead to frustration, damaged equipment, or worse.
Start by assessing your power needs. How much single-phase power do you need? Are you running a single appliance, or an entire workshop? Rotary phase converters are generally better for high-power applications, while static converters are more suitable for smaller loads or motor starting. If your existing 3-phase system includes a suitable transformer, tapping into it might be an option, but this is usually only practical for very specific situations.
Consider the type of equipment you'll be powering. Some equipment is more sensitive to voltage fluctuations and power quality than others. Rotary phase converters generally provide cleaner power than static converters, which can be important for sensitive electronics. If you're running CNC machines, precision instruments, or other delicate equipment, a rotary converter might be worth the extra investment.
Don't forget to factor in the cost. Rotary phase converters are typically more expensive upfront than static converters, but they can be more cost-effective in the long run if you need a significant amount of single-phase power. Static converters are cheaper to purchase, but they may not be suitable for all applications, and they can potentially damage your equipment if they're not properly matched to the load. So, weigh the initial cost against the long-term benefits and potential risks.
Last but not least, think about the future. Are your power needs likely to increase in the future? If so, it might be worth investing in a more robust solution, like a rotary phase converter, that can handle your current and future power requirements. It's always better to have a little extra capacity than to be constantly pushing the limits of your equipment. Planning ahead can save you time, money, and headaches in the long run.
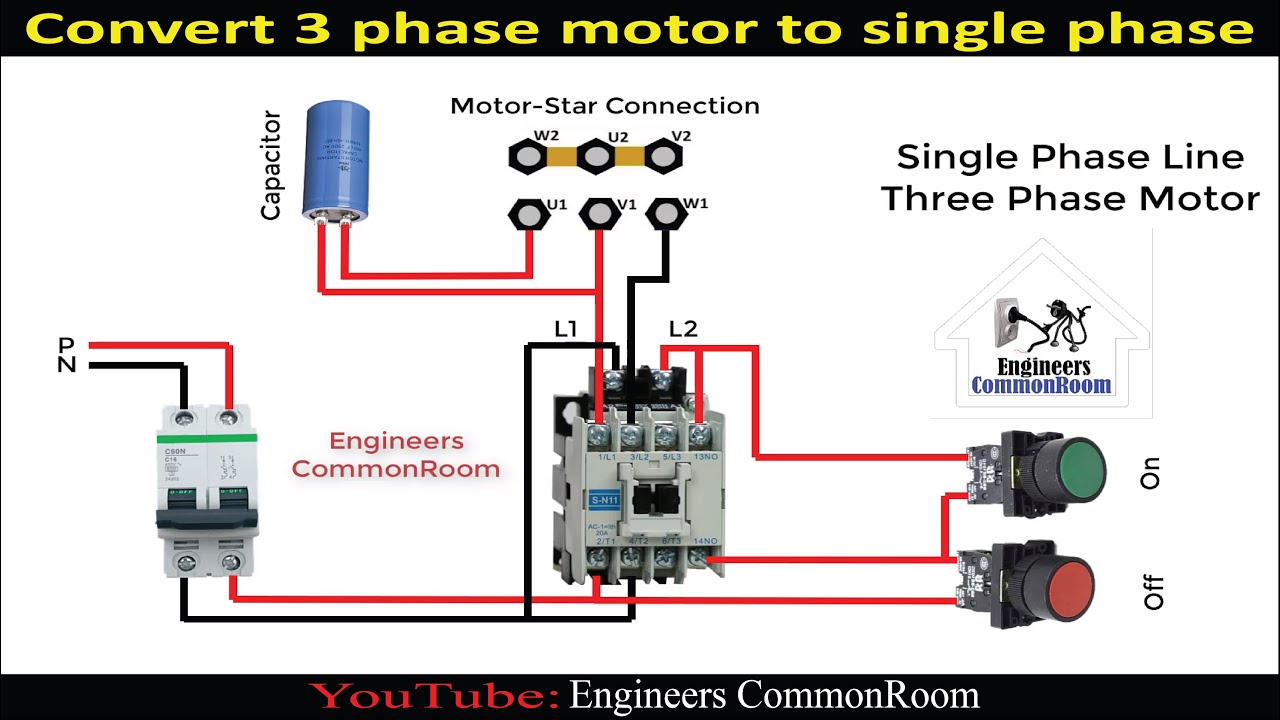
Getting Professional Help
5. Knowing When to Throw in the Towel
Look, some projects are perfect for a DIY approach. Hanging a picture? Go for it! Building a birdhouse? Knock yourself out! But when it comes to messing with high-voltage electricity, it's often best to call in the pros. There's no shame in admitting that you're not an expert, and hiring a qualified electrician can save you time, money, and potentially your life.
If you're not comfortable working with electricity, or if you don't have the proper training and experience, stop right there. This isn't a learning opportunity; it's a potential death trap. Electrical work requires specialized knowledge and skills, and making a mistake can have serious consequences. An electrician has the expertise to properly assess your power needs, select the right conversion method, and install it safely and efficiently.
Another good reason to call an electrician is if you're not sure about the electrical codes and regulations in your area. These codes can be complex and confusing, and violating them can result in fines and penalties. An electrician is familiar with these codes and can ensure that your electrical installation complies with all applicable requirements. They can also help you obtain the necessary permits and inspections.
Finally, if you're experiencing any problems with your electrical system, such as frequent circuit breaker trips, flickering lights, or unexplained power outages, it's time to call an electrician. These symptoms can indicate a serious electrical problem that needs to be addressed immediately. Ignoring these problems can lead to more serious damage, including electrical fires. Don't wait until it's too late; call an electrician as soon as you notice any signs of trouble.