Favorite Tips About Why Doesn T Everyone Use Geothermal
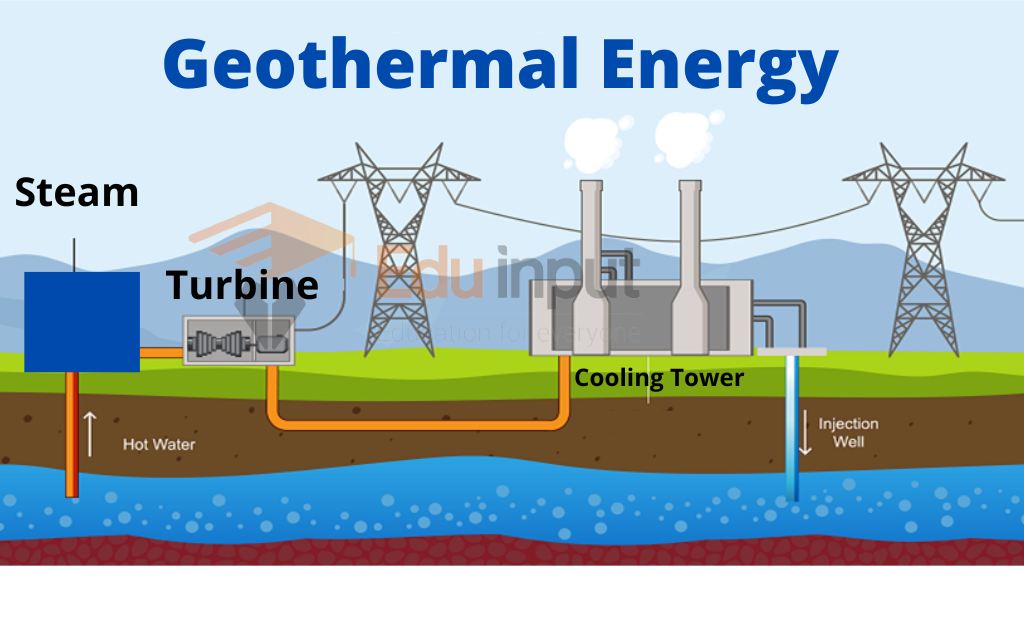
Geothermal Energy
1. The Promise of Geothermal
Ever wonder why, with all the buzz about renewable energy, geothermal isn't plastered on every rooftop? Geothermal energy, the Earth's own internal heating system, seems like a no-brainer. We're talking about tapping into a practically limitless supply of heat bubbling beneath our feet. Imagine cozy homes in winter, cool spaces in summer, all powered by the planet's natural warmth. Sounds like a dream, right?
Well, like many dreams, there are a few practicalities to consider. Geothermal energy, while incredibly promising, isn't quite as simple as sticking a straw into the ground and sipping up free energy. There are some significant hurdles that keep it from being the go-to energy source for everyone.
Think of it like this: geothermal is the organic, locally-sourced farm-to-table dinner of the energy world. Its fantastic, sustainable, and good for you, but sometimes you just need a quick and easy microwave meal, even if it's not the healthiest choice. Other energy sources, especially fossil fuels, have been our "microwave meals" for far too long. Let's dig a little deeper into why geothermal isnt quite as widespread as it maybe should be.
We need to peel back the layers of the Earth, metaphorically speaking, to truly understand why "Why doesn t everyone use geothermal" is a question that needs an answer. Is it the cost? The location? The complexity? Let's find out!

The Price Tag
2. The Upfront Investment
Here's the big one: cost. Setting up a geothermal system isn't exactly pocket change. We're not talking about swapping out a lightbulb. The initial investment can be significant, whether you're building a large-scale power plant or installing a system for your home. Drilling deep into the earth and installing the necessary infrastructure demands serious capital. Think of it as buying a lifetime supply of artisanal coffee upfront — the long-term benefits are there, but the initial cost can be daunting.
For residential geothermal systems, even with government incentives and long-term savings on energy bills, many homeowners are hesitant to make that initial leap. Renters, especially, arent going to invest in a system that benefits the landlord. It's a classic case of short-term pain for long-term gain, and not everyone is willing or able to shoulder that pain upfront. Its the sticker shock factor that often deters people.
Now, imagine the scale of geothermal power plants! These projects involve extensive geological surveys, drilling, construction, and complex engineering. The high capital costs can deter investors and make it difficult to secure financing. Developing those power plants takes time and big money which requires careful planning and risk analysis.
However, it's important to consider the long game. While the upfront cost is high, geothermal systems boast lower operational costs than traditional energy sources. Once the system is up and running, the fuel — the Earth's heat — is free. That means significantly lower monthly energy bills and reduced dependence on volatile fossil fuel markets. Its the difference between paying rent forever and eventually owning your own home.

How Is Geothermal Energy Generated
Location, Location, Location
3. Geographic Limitations
Okay, so you're sold on the idea of geothermal. You're ready to dig a hole in your backyard and tap into the Earth's fiery core. Unfortunately, geothermal resources aren't evenly distributed across the planet. Some regions are simply more geologically blessed than others. Places with volcanic activity, hot springs, and naturally high subsurface temperatures are prime geothermal real estate.
Countries like Iceland, the Philippines, and Indonesia, with their abundant geothermal resources, have embraced geothermal energy on a large scale. They're practically sitting on top of a gold mine of heat! But what about places that aren't located near geothermal hotspots? That's where things get tricky. While enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) can expand the reach of geothermal energy, they're still in their early stages of development and require significant technological advancements.
Think of it as trying to grow tropical fruit in Alaska. It's not impossible, but it requires a lot more effort and resources than growing it in a tropical climate. Similarly, harnessing geothermal energy in areas with low geothermal gradients requires deeper drilling, more complex technology, and higher costs, which makes it less economically viable. Therefore, not everyone can simply plug into geothermal energy wherever they want.
Therefore, the question of "Why doesn t everyone use geothermal" depends heavily on geography. While technology is improving and allowing us to access geothermal energy in more places, the Earth's natural distribution of heat remains a significant factor. Location is absolutely everything in geothermal real estate!

Geothermal Heating
Technical Hurdles
4. Complexity and Challenges
Geothermal energy isn't as simple as drilling a hole and letting the steam do the work (although that's part of it in some places). There are several technical challenges that need to be addressed. For starters, drilling deep into the Earth can be complex and expensive, particularly in areas with hard rock formations. It's not exactly like drilling for oil, but it definitely requires specialized equipment and expertise. We're talking serious engineering!
Furthermore, geothermal fluids can contain dissolved minerals and gases that can corrode pipes and equipment. Scale buildup, corrosion, and managing these fluids are major technical considerations that can impact the efficiency and longevity of geothermal systems. Think of it as dealing with the plumbing in an old house you never know what you're going to find! Proper maintenance and material selection are crucial to prevent these problems and ensure the system runs smoothly.
And, lets not forget about potential induced seismicity. In some cases, injecting fluids into the ground during enhanced geothermal systems can trigger minor earthquakes. While these events are usually small, they can raise concerns and require careful monitoring and mitigation strategies. It is very important to minimize environmental effects when extracting heat from the ground.
These challenges, along with the need for skilled professionals to design, install, and maintain geothermal systems, all contribute to the complexity and cost of geothermal energy. It's not just about digging a hole; it's about understanding the Earth's geology, chemistry, and physics to ensure a safe, efficient, and sustainable geothermal operation. It's a science as much as an engineering feat!

Geothermal Energy Diagram For Kids At Tanscarletteblog Blog
Policy and Perception
5. Overcoming Barriers
Even if the technology and cost challenges are addressed, geothermal energy faces other hurdles, including policy and perception. Government regulations, permitting processes, and lack of public awareness can all slow down the adoption of geothermal energy. Sometimes, it's not just about what's possible, but about what's allowed and what people believe.
Many countries still heavily subsidize fossil fuels, creating an uneven playing field for renewable energy sources like geothermal. Leveling the playing field with favorable policies, tax incentives, and streamlined permitting processes can encourage more investment in geothermal energy. It is not enough to simply advocate for change; you must create the opportunity for change.
Theres also the issue of public perception. Many people simply aren't aware of the benefits of geothermal energy. Educating the public about the environmental advantages, long-term cost savings, and reliability of geothermal systems can help overcome misconceptions and promote wider adoption. It's about showing people that geothermal isn't just some futuristic technology but a viable and sustainable energy solution that's available today.
Addressing "Why doesn t everyone use geothermal" requires a multi-pronged approach. Technology, economics, policy, and public perception all play a crucial role. By tackling these challenges head-on, we can unlock the full potential of geothermal energy and move toward a cleaner, more sustainable energy future. The Earth is waiting; all we need to do is listen.

FAQ
6. Common Inquiries
Lets tackle a few frequently asked questions about geothermal energy to clear up any lingering doubts.
Q: Is geothermal energy really renewable?A: Absolutely! The Earth's heat is constantly replenished by radioactive decay in the planet's core. As long as we manage geothermal resources responsibly, its a practically inexhaustible source of energy.
Q: Can geothermal energy cause earthquakes?A: While enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) can sometimes trigger minor earthquakes, these events are usually small and rare. Careful monitoring and mitigation strategies can minimize the risk.
Q: How long does a geothermal system last?A: A well-maintained geothermal system can last for decades. The underground components can last for 50 years or more, while the heat pump itself typically lasts for 15-20 years.