Painstaking Lessons Of Tips About What Is A PPP Connection

How To Set Up And Use Pppoe Connection On Windows 10 Images
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Peering into the Point-to-Point Protocol
Okay, let's be honest. When you first stumble across the term "PPP connection," it sounds like something out of a spy movie, doesn't it? "Agent, establish a secure PPP link!" But the reality is far less glamorous (though arguably just as important, depending on your reliance on the internet!). PPP, or Point-to-Point Protocol, is essentially a way for two devices to directly communicate with each other over a serial connection. Think of it as a digital handshake between your computer and your Internet Service Provider (ISP), allowing you to access the vast wonderland that is the World Wide Web. It's not new tech, but it has been, and still is, the foundation for a lot of internet connections you might not even realize are there.
This digital handshake isnt just about saying hello. PPP provides a standard method for encapsulating Network Layer protocols (like IP, the internet's workhorse) over these serial links. It handles authentication, ensuring it's really you connecting, and provides negotiation for things like IP addresses and other configuration settings. It's like a well-mannered, highly efficient concierge for your internet connection. It sets everything up neatly and then steps back so you can browse funny cat videos without a hitch.
Before we delve too deep into the technical weeds, let's keep this simple: a PPP connection bridges the gap between your personal device and the wider internet. Without it, your modem would just be a fancy paperweight (or maybe a really cool retro decoration). While other protocols exist now, PPP was instrumental in bringing dial-up internet to the masses, and even continues to be utilized in some broadband configurations today. So, next time you're online, give a silent nod to PPP for helping make it all possible.
But where does this old timer of a protocol still show up? Well, surprisingly, it's not completely relegated to the history books! While you might not be using dial-up (we sincerely hope not!), PPP is still found in certain types of DSL connections and in some mobile broadband setups. It might be under the hood, chugging away, without you even knowing. It is the unsung hero of connectivity, quietly doing its job while you stream your favorite show. It's like the plumbing in your house - you only think about it when it doesn't work!

Point To Protocol PPP
Digging Deeper
2. Understanding the Inner Workings of PPP
Alright, so we know what a PPP connection is, but how does it do what it does? Let's break it down. Imagine you're sending a letter. You don't just slap a stamp on your message; you put it in an envelope, address it, and then send it on its way. PPP does something similar with internet data. It takes the data (your webpage request, for instance) and packages it into a "PPP frame." This frame contains your data, along with extra information like the type of data, error-checking codes, and addressing details.
This process of packaging the data is called encapsulation, and it's a crucial part of PPP's operation. The PPP frame is then transmitted over the serial link to the other device (usually your ISP's server). That server unpacks the frame, extracts the data, and sends it on its way to the wider internet. When data comes back to you, the process is reversed. The ISP packages the response into a PPP frame and sends it to your computer, which unpacks the frame and displays the webpage for you to see. Think of the PPP connection as a dedicated postal worker, carefully handling your precious data packets.
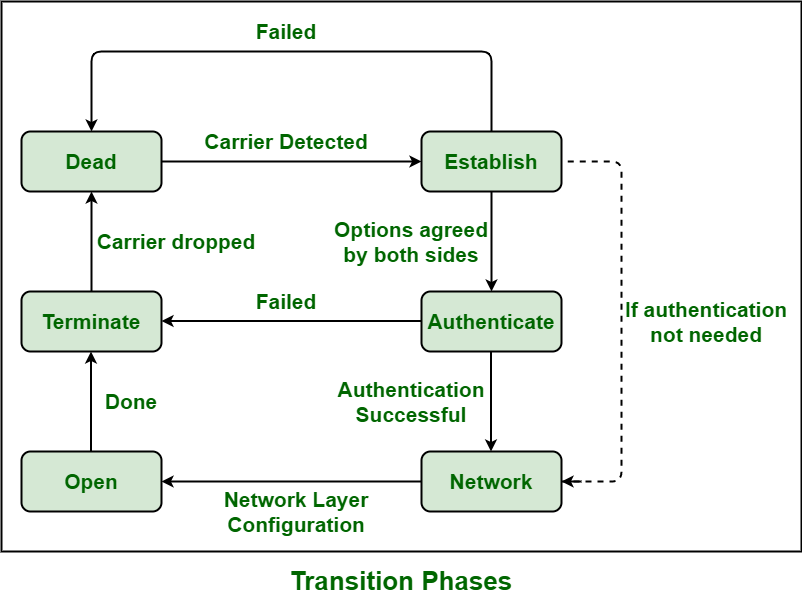
Authentication is another key function. PPP uses protocols like PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) or CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) to verify your identity. PAP is simpler but transmits passwords in plain text (not ideal!). CHAP is more secure, using a "challenge-response" mechanism to verify your identity without ever sending your actual password across the network. It's like having a secret handshake instead of just blurting out your password to anyone who asks.
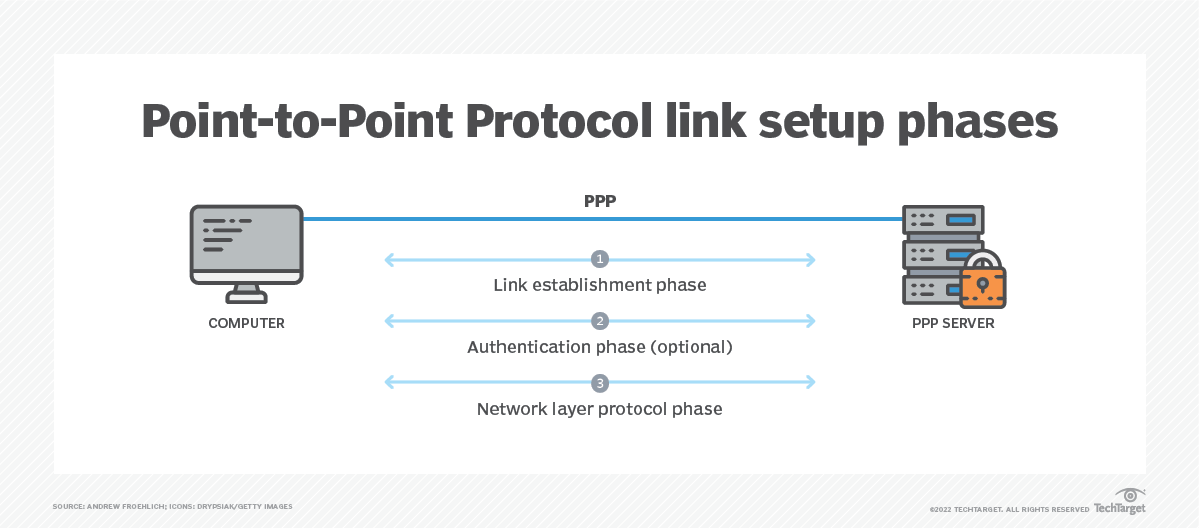
Furthermore, PPP handles negotiation. When the connection is established, your computer and the ISP's server "talk" to each other, negotiating settings like IP addresses, DNS servers, and compression methods. This ensures that both devices are on the same page and can communicate effectively. It's like agreeing on the rules of the game before you start playing. This negotiation part is critical as it optimizes the connection to the most efficient settings for the best possible connection speed.
What Is PPP (PointtoPoint Protocol) And How Does It Work?
PPP vs. Other Protocols
3. Comparing PPP to Modern Connection Methods
Okay, let's face it. In the world of high-speed fiber and ubiquitous Wi-Fi, PPP might seem like a relic of a bygone era. And in some ways, it is. Newer protocols, like Ethernet and various broadband technologies, offer significantly faster speeds and greater efficiency. But that doesn't mean PPP is completely irrelevant. It's more like a veteran player who's still got some tricks up their sleeve.
Ethernet, for instance, is the dominant protocol for local area networks (LANs). It's the technology that connects your computer to your router via a cable. Ethernet is much faster and more scalable than PPP. But Ethernet doesn't handle authentication or negotiation in the same way that PPP does. It relies on other protocols, like DHCP, to assign IP addresses and configure network settings. This is not necessarily a good or bad thing, it just highlights that PPP has a different role.
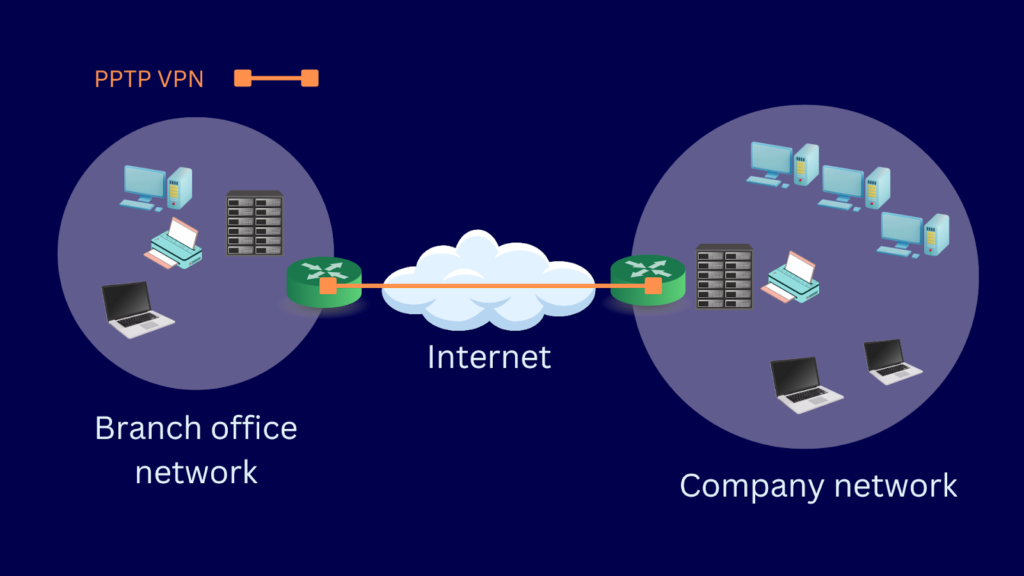
Broadband technologies, like DSL and cable internet, often use PPP as a transport mechanism for the initial connection setup. For example, PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) is a common protocol for DSL connections. It allows the ISP to authenticate users and manage IP addresses over an Ethernet connection. So, while you might be using Ethernet to connect to your router, PPP might still be working behind the scenes to establish the initial connection to your ISP.
In the modern world, PPP is less about being the primary connection protocol and more about providing a foundational layer for other technologies. It's like the cement that holds the bricks together in a building. You might not see it, but it's essential for the structure's stability. While it's not the flashiest or fastest protocol, PPP continues to play a vital role in ensuring reliable internet connectivity in many parts of the world.
Troubleshooting Common PPP Connection Issues
4. When the Digital Handshake Goes Wrong
Like any technology, PPP connections can sometimes run into problems. If you're having trouble connecting to the internet, a PPP issue might be to blame. One common issue is authentication failure. This could be due to a misspelled password, an incorrect username, or a problem with your ISP's authentication servers. Double-check your credentials and contact your ISP to make sure everything is configured correctly on their end.
Another potential problem is a configuration issue. Incorrect IP address settings, DNS server addresses, or other network parameters can prevent a PPP connection from being established. Make sure your computer is configured to obtain these settings automatically (DHCP) or that you've entered the correct information manually. Your ISP can provide you with the necessary configuration details if needed. Ensure that all network cables are properly connected and that your modem or router is functioning correctly.
Sometimes, the problem might be with your modem or router itself. Try restarting your modem and router. This can often resolve temporary glitches and restore your internet connection. If the problem persists, check the device's documentation for troubleshooting steps or contact the manufacturer for support. Make sure the firmware on your modem and router is up to date. Outdated firmware can sometimes cause compatibility issues and connectivity problems.
In rare cases, the issue might be with the PPP server at your ISP. If you've tried all the troubleshooting steps on your end and you're still unable to connect, contact your ISP's technical support team. They can investigate the issue on their servers and provide further assistance. Remember, clear communication with your ISP is key to resolving PPP connection issues efficiently. Explain the steps you've already taken and provide any relevant error messages or logs.

The Future of PPP
5. Assessing the Longevity of the Point-to-Point Protocol
Predicting the future of technology is always a tricky game. But when it comes to PPP, it's safe to say that its role will continue to evolve. While it might not be the dominant connection protocol it once was, PPP is likely to remain relevant in certain niche applications for the foreseeable future. Its simplicity, reliability, and well-established standards make it a valuable tool for specific scenarios.
For instance, PPP might continue to be used in some embedded systems and industrial applications where a simple, point-to-point connection is required. It could also find a place in emerging technologies like IoT (Internet of Things), where low-bandwidth, low-power communication is essential. And as mentioned earlier, it may very well keep ticking away in the background in some DSL and mobile connections.
However, it's also clear that newer protocols and technologies will continue to push PPP to the periphery. High-speed fiber, 5G, and other advanced networking technologies offer significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater scalability. These advancements will inevitably replace PPP in many of its current applications.
Ultimately, the future of PPP will depend on its ability to adapt to the changing landscape of networking technology. While it might not be the star player anymore, PPP can still contribute to the overall connectivity ecosystem. Its legacy as a foundational protocol will undoubtedly endure, even as newer technologies take center stage. Like a trusty old tool, PPP might not be used every day, but it's good to have around when you need it.